Understanding Valence in Psychology: A Comprehensive Guide to Emotional Charge
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes
Key Takeaways
-
- Valence refers to the positive or negative emotional charge associated with an event, object, or situation.
-
- Understanding valence helps explain human behavior and decision-making processes.
-
- Valence plays a crucial role in areas like decision making, memory formation, and behavioral motivation.
-
- Applications of valence are found in clinical psychology, marketing, and education.
- Measuring valence involves self-report measures, physiological measurements, and behavioral observations.
Table of Contents
What is Valence in Psychology?
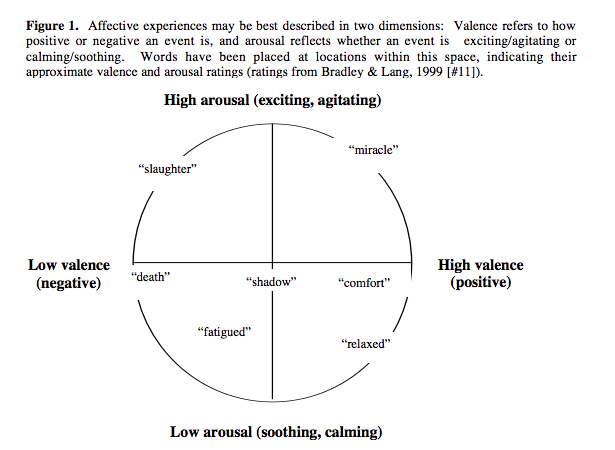
At its core, valence refers to the intrinsic attractiveness (positive valence) or aversiveness (negative valence) of an event, object, or situation. Think of it as an emotional temperature gauge that measures whether something makes us feel good or bad. Just as a thermometer measures physical temperature, valence measures emotional temperature.
The Spectrum of Emotional Valence
Psychological valence operates on a spectrum:
-
- Positive valence: Associated with pleasure, happiness, and approach behaviors
-
- Neutral valence: Neither positive nor negative emotional charge
- Negative valence: Connected to displeasure, unhappiness, and avoidance behaviors
Understanding valence helps researchers and practitioners analyze how people respond to different stimuli and why they make certain choices.
The Science Behind Valence
Research from multiple institutions has demonstrated the crucial role of valence in various psychological processes:
1. Decision Making
Studies show that valence significantly influences our decision-making processes. When faced with choices, we often unconsciously evaluate the emotional valence of each option before making a selection. https://humanbehaviour.co.uk/psychology-of-political-affiliation
2. Memory Formation
Research indicates that events with strong emotional valence (either positive or negative) are more likely to be remembered than neutral events. This explains why we often have vivid memories of both particularly happy and particularly traumatic experiences. https://humanbehaviour.co.uk/evolving-digitally-removing-history/
3. Behavioral Motivation
The concept of valence helps explain why we approach certain situations and avoid others. Positive valence typically encourages approach behaviors, while negative valence triggers avoidance responses. https://humanbehaviour.co.uk/how-environment-affects-behaviour
Applications of Valence in Psychology
Understanding valence has practical applications across various fields:
1. Clinical Psychology
-
- Therapists use valence assessment to understand patients’ emotional responses
-
- Treatment plans often focus on modifying negative valence associations
- Helps in treating conditions like anxiety and depression
2. Marketing and Consumer Behavior
-
- Advertisers leverage positive valence to create appealing campaigns
-
- Product packaging and design often aim to trigger positive emotional responses
- Brand associations are built on creating positive valence connections https://humanbehaviour.co.uk/how-social-media-affects-behaviour
3. Educational Psychology
-
- Teachers use positive valence to enhance learning experiences
-
- Classroom environments are designed to promote positive emotional associations
- Learning materials are structured to create engaging, positive experiences
Measuring and Assessing Valence
Psychologists use various methods to measure emotional valence:
1. Self-Report Measures
-
- Questionnaires and surveys
-
- Emotional rating scales
- Diary studies
2. Physiological Measurements
-
- Heart rate monitoring
-
- Skin conductance tests
- Brain activity scanning
3. Behavioral Observations
-
- Facial expression analysis
-
- Body language assessment
- Approach-avoidance behaviors
The Role of Valence in Mental Health
Understanding valence is crucial in mental health treatment:
1. Depression
-
- Often characterized by a bias toward negative valence
-
- Treatment involves rebalancing valence interpretations
-
- Cognitive restructuring helps modify negative valence patterns
2. Anxiety Disorders
-
- Frequently involves heightened sensitivity to negative valence
-
- Exposure therapy helps normalize valence responses
- Mindfulness techniques aid in managing valence reactions
3. PTSD
-
- Involves intense negative valence associated with traumatic memories
-
- Treatment focuses on processing and integrating these experiences
- Therapy helps develop healthier valence responses
Valence in Daily Life
Understanding valence can help individuals:
-
- Make more conscious decisions
-
- Improve emotional awareness
-
- Develop better coping strategies
-
- Enhance relationships
- Create more positive experiences
Future Directions in Valence Research
Current research is exploring:
-
- The role of valence in artificial intelligence and emotion recognition
-
- Cultural differences in valence interpretation
-
- The impact of valence on social media behavior
- Neurological bases of valence processing
Tips for Managing Emotional Valence
1. Self-Awareness
-
- Pay attention to your emotional responses
-
- Notice patterns in what triggers positive or negative valence
- Keep an emotional diary
2. Conscious Regulation
-
- Practice mindfulness
-
- Develop coping strategies
- Learn to reframe negative experiences
3. Environment Design
-
- Create spaces that promote positive valence
-
- Minimize exposure to negative triggers
- Surround yourself with uplifting influences
Conclusion
Valence in psychology provides a crucial framework for understanding emotional experiences and their impact on behavior. Whether in clinical settings, educational environments, or daily life, recognizing and working with valence can lead to better emotional regulation, decision-making, and overall well-being. As research continues to advance our understanding of valence, its applications in psychology and related fields will likely expand, offering new insights into human behavior and emotional processing.
Remember that while understanding valence is important, emotional experiences are complex and multifaceted. Working with mental health professionals can provide personalized guidance in applying these concepts to your specific situation.

